I've lost a few anaheims over the last few weeks to pepper maggots, and I haven't been to concerned, I mean, their only anaheims. But I've been away for a few days, I just got back, and I've just had to throw out 6 semi-ripe and ripe nagas. This means war. What can I do to kill them? I'm open to any and all suggestions, I need them to be gone.
-
Do you need help identifying a 🌶?
Is your plant suffering from an unknown issue? 🤧
Then ask in Identification and Diagnosis.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
At war with pepper maggots
- Thread starter BobsYourUncle
- Start date
Thanks guys... I'll have a look at bunnings tomorrow, see what I can get.
I too had a problem with pepper maggots this year, you have to destroy the fly before it starts to inject the dreaded beast into the peppers after the fly has done its dirty work you just have to let it run its course. You cannot kill the maggots because they are already in the pods. I literally lost thousands of pods this year to the maggots. this is a bad pic but this is one of the little buggers.
Dale
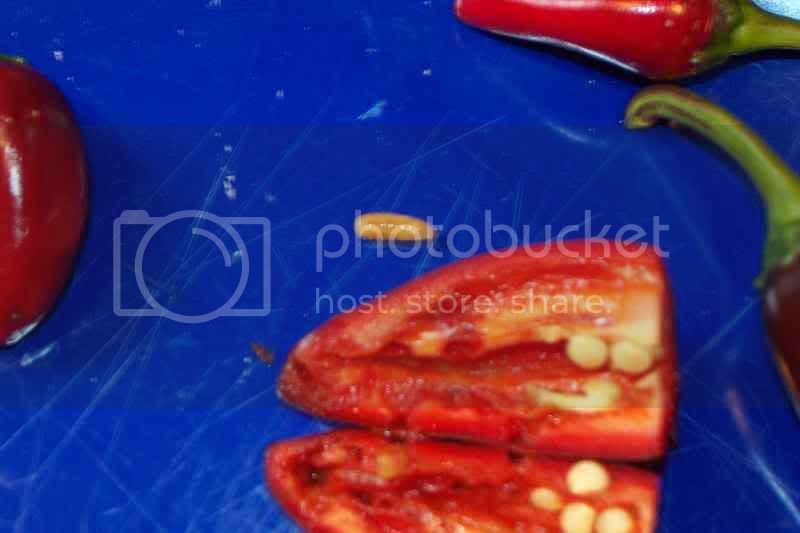
Dale

Interesting!
I wonder if you eat the maggot if it tastes hot?
You could powder the maggots and sell hot pepper sauce with a small bag of maggot dust.
Kinda like a what they do with Mezcal.
humm.....
http://www.mezcal.com/worms.html
I wonder if you eat the maggot if it tastes hot?
You could powder the maggots and sell hot pepper sauce with a small bag of maggot dust.
Kinda like a what they do with Mezcal.
humm.....
http://www.mezcal.com/worms.html
Well, I just covered everything with pyrethrum, hopefully that'll keep the flies away. Looks like I'm going to lose quite a few more pods though - hopefully no more nagas, I've already lost at least 10 of them :'( - but just about all my corno di toros, and a good handful of red habs.
http://www.diyhomeguide.com/yard-ga...advanced&ovadid=8270033011&ovkwid=52462587011
Maybe thi will help also. Glad I read this thread because it will help me out when I start planting my seeds.
Maybe thi will help also. Glad I read this thread because it will help me out when I start planting my seeds.
what i have been trying to find info on is how to get rid of the pupa which are buried in the ground. Here is something that I found on thier life cycle.
Dale
Life History - Pepper maggots overwinter as pupae 5 to 10 cm below the soil surface. Flies emerge from late June through August and mate. Soon afterwards, females insert eggs just beneath the skin of young peppers. Eggs hatch about 10 days later depending on the growth rate of host peppers. At this time the peppers are usually 2/3 to fully grown. Larvae feed within the peppers for about 18 days. When fully grown, each larva cuts an exit hole, emerges, and drops to the soil to pupate. Only one generation occurs each year.
Dale
Life History - Pepper maggots overwinter as pupae 5 to 10 cm below the soil surface. Flies emerge from late June through August and mate. Soon afterwards, females insert eggs just beneath the skin of young peppers. Eggs hatch about 10 days later depending on the growth rate of host peppers. At this time the peppers are usually 2/3 to fully grown. Larvae feed within the peppers for about 18 days. When fully grown, each larva cuts an exit hole, emerges, and drops to the soil to pupate. Only one generation occurs each year.
Thanks thepodpiper... I've been pulling off any affected pods I've seen, sounds like this is a good way to go, stops future generations.
I think I am going to cover the dirt as soon as the snow melts this year so that i can heat it up and see if that will help in killing the pupae then I will spray the foilage as suggested the months that they are to emerge and lay thier eggs. i do not want a year like last year watching all those pods rot away.
Dale
Dale
thepodpiper said:I think I am going to cover the dirt as soon as the snow melts this year so that i can heat it up and see if that will help in killing the pupae then I will spray the foilage as suggested the months that they are to emerge and lay thier eggs. i do not want a year like last year watching all those pods rot away.
Dale
Two things:
1. I wonder if beneficial nematodes would help? I've found them to be useful in controlling things like fire ants and fleas.
2. I wonder if an insect growth regulator like Nylar would work? There are photo stable products with Nylar in them, so it could be used in the garden. I've used them to help with fleas, but if you could soak the soil, or apply it during the season this year, it seems like it would help break the life cycle and eradicate the bugs.
It would probably affect beneficial insects as well, but they're not too effective against the pepper maggots anyway.
Ok so here's an update. I've identified the exact problem: fruit fly. I've setup a trap using some sort of bait thingy from bunnings which lures and kills the male flies, and it's got a good dozen or so already. I also got a fruit fly spray solution on the weekend, so hopefully I'll be able to win this war. Bad news however is that I've lost a few of my precious bullock heart tomatoes to the bastards.
so do you have a fruit fly problem or a pepper maggot problem or both.
Dale
Dale
I'm pretty sure it's fruit flies (and fruit fly larvae) not pepper maggots.
Tony05, hope this helps.
Dale
Life History - Pepper maggots overwinter as pupae 5 to 10 cm below the soil surface. Flies emerge from late June through August and mate. Soon afterwards, females insert eggs just beneath the skin of young peppers. Eggs hatch about 10 days later depending on the growth rate of host peppers. At this time the peppers are usually 2/3 to fully grown. Larvae feed within the peppers for about 18 days. When fully grown, each larva cuts an exit hole, emerges, and drops to the soil to pupate. Only one generation occurs each year.
There are four stages in the life cycle of the fruit fly: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. At a typical classroom temperature (21 C), Drosophila melanogaster will produce new adults in two weeks; eight days in the egg and larval stages, and six days in the pupal stage. The life span of a fruit fly may be several weeks.
Twenty-four hours after the egg is laid, the larva hatches. The larva has two molting periods, during which the cuticle, mouth, hooks, and spiracles are shed. The larva is called an instar during the periods of growth before and after molting. Thus, the fruit fly has three instars. The puparium develops from the third instar which becomes hard in texture and dark in color.
The puparium is where metamorphosis takes place. Just before the adult fly emerges from the puparium, the pupa darkens. Approximately 24 hours before the adult fly emerges, one can see the folded wings and the pigment of the eyes if one looks closely through the puparium.
Upon completion of metamorphosis, the adult forces its way through the operculum (anterior end) of the puparium. Initially the fruit fly appears light in color with a long abdomen and unexpanded wings. In just a few hours the fly gets darker in color, rounder in the abdomen and extends its wings. Approximately 48 hours after emerging from the puparium, it is possible for females to start laying eggs. However, there are only 12 hours that a female can be considered virgin after emerging as an adult. After reaching this maturity, the flies are fertile for life. A female fruit fly can store sperm after a single insemination and use it for many reproductions; therefore it is important to use virgin females for genetic crosses.
Dale
Life History - Pepper maggots overwinter as pupae 5 to 10 cm below the soil surface. Flies emerge from late June through August and mate. Soon afterwards, females insert eggs just beneath the skin of young peppers. Eggs hatch about 10 days later depending on the growth rate of host peppers. At this time the peppers are usually 2/3 to fully grown. Larvae feed within the peppers for about 18 days. When fully grown, each larva cuts an exit hole, emerges, and drops to the soil to pupate. Only one generation occurs each year.
There are four stages in the life cycle of the fruit fly: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. At a typical classroom temperature (21 C), Drosophila melanogaster will produce new adults in two weeks; eight days in the egg and larval stages, and six days in the pupal stage. The life span of a fruit fly may be several weeks.
Twenty-four hours after the egg is laid, the larva hatches. The larva has two molting periods, during which the cuticle, mouth, hooks, and spiracles are shed. The larva is called an instar during the periods of growth before and after molting. Thus, the fruit fly has three instars. The puparium develops from the third instar which becomes hard in texture and dark in color.
The puparium is where metamorphosis takes place. Just before the adult fly emerges from the puparium, the pupa darkens. Approximately 24 hours before the adult fly emerges, one can see the folded wings and the pigment of the eyes if one looks closely through the puparium.
Upon completion of metamorphosis, the adult forces its way through the operculum (anterior end) of the puparium. Initially the fruit fly appears light in color with a long abdomen and unexpanded wings. In just a few hours the fly gets darker in color, rounder in the abdomen and extends its wings. Approximately 48 hours after emerging from the puparium, it is possible for females to start laying eggs. However, there are only 12 hours that a female can be considered virgin after emerging as an adult. After reaching this maturity, the flies are fertile for life. A female fruit fly can store sperm after a single insemination and use it for many reproductions; therefore it is important to use virgin females for genetic crosses.

